Marketing Experimentation: A Practical Guide
What is Marketing Experimentation?
Marketing experimentation is a data-driven approach to testing different marketing tactics to identify what works best for your specific audience. By systematically testing variations of your marketing campaigns, you can gain valuable insights and optimise your strategies for maximum impact.
By using marketing experimentation on a regular basis you’ll be able to improve your campaigns and develop new skills as a marketer
“Ditch the Playbook, Write Your Own: Experimentation is the Key to Marketing Mastery”
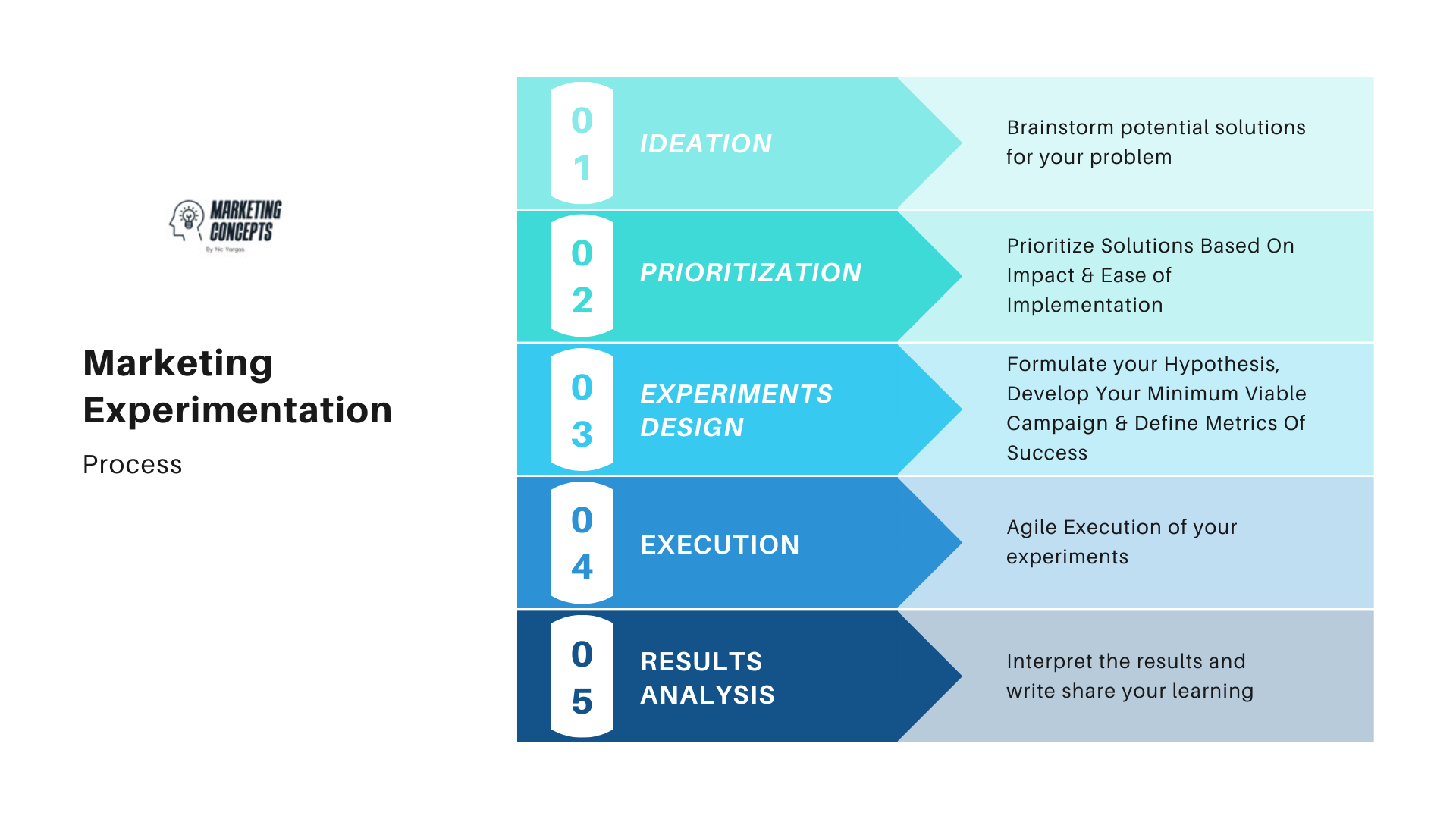
Marketing Experimentation Process by marketingconcepts.co
Why is Marketing Experimentation Important?
Data-Driven Decision Making: Relies on concrete data to inform decisions rather than assumptions.
Increased ROI: Identifies high-performing strategies and allocates resources effectively.
Competitive Advantage: Stay ahead of the curve by constantly innovating and testing new ideas.
Enhanced Customer Understanding: Gain deeper insights into your audience's preferences and behaviours.
Practical Use Cases for Marketers at Different Levels
Beginner Marketers:
A/B Testing Email Subject Lines: Experiment with different subject lines to see which ones drive higher open rates. For example, try a subject line that highlights a benefit ("Boost Your Sales in 7 Days") versus a more direct approach ("New Product Alert").
Landing Page Optimisation: Test different headline copy, hero images, and call-to-action buttons to improve conversion rates.
Social Media Experimentation: Try different posting times, content formats, and engagement tactics to increase follower growth and engagement. For instance, experiment with posting videos versus images on Instagram to see which format performs better.
Intermediate Marketers:
Multivariate Testing: Test multiple variables simultaneously to identify the optimal combination of elements (e.g., headline, body copy, and call-to-action). For example, test different headline and image combinations on your landing page to see which combination drives the highest conversion rate.
Personalisation Experiments: Tailor your marketing messages to specific segments of your audience based on demographics, behaviour, or preferences. For instance, send personalised email campaigns to different customer segments based on their purchase history.
Split Testing: Divide your audience into two or more groups and expose them to different marketing treatments to measure the impact. You could split test different ad creatives on Google Ads to see which one performs better.
Advanced Marketers:
Bayesian A/B Testing: Utilise statistical methods to make faster and more accurate decisions with less data.
Bandit Algorithms: Optimise your experiments in real-time by continuously allocating more traffic to the winning variations.
Machine Learning-Powered Experimentation: Leverage AI to automate the experimentation process and identify the most promising variations.
Key Principles of Marketing Experimentation
Define a Clear Hypothesis: Clearly state what you expect to happen as a result of the experiment.
Isolate Variables: Test one variable at a time to accurately measure the impact.
Set a Sample Size: Ensure you have enough data to draw statistically significant conclusions.
Measure Key Metrics: Track relevant metrics, such as conversions, click-through rates, and revenue.
Analyse Results: Use data analysis tools to identify patterns and trends.
Iterate and Optimise: Continuously refine your strategies based on the results of your experiments.
By embracing a culture of experimentation, you can unlock your full potential as a marketer and drive significant growth for your business.
Remember, the key to successful marketing experimentation is to start small, test often, and learn from your results.
Further Readings
Designing Marketing Experiments
A marketing experiment is a powerful tool to test hypotheses, measure the impact of marketing strategies, and optimise campaigns. Here's a detailed process to guide marketers of all levels:
Beginner Level
Identify a Problem or Opportunity:
Simple Questions: Start with straightforward questions like, "Does changing the call-to-action button colour increase clicks?" or "Does offering a discount code in email subject lines improve open rates?"
Formulate a Hypothesis:
Basic Hypothesis: A simple hypothesis could be, "If we change the button colour to red, then click-through rates will increase."
Design a Simple Experiment:
A/B Testing: Create two versions of a marketing asset (e.g., email, landing page) with one key difference (e.g., button colour).
Random Assignment: Randomly assign users to either version to minimise bias.
Set Up Tracking:
Basic Metrics: Use analytics tools to track relevant metrics like clicks, conversions, or open rates.
Run the Experiment:
Short Duration: Start with shorter experiments to gather quick insights.
Analyse Results:
Simple Comparison: Compare the performance of the two versions using basic statistical analysis or A/B testing tools.
Intermediate Level
Identify a Clear Objective:
Specific Goals: Define specific goals like increasing sales, improving customer retention, or boosting brand awareness.
Formulate a Testable Hypothesis:
Clear and Measurable: Frame hypotheses in a way that can be tested, such as, "If we personalise email subject lines, then open rates will increase by 10%."
Design a Rigorous Experiment:
Multiple Variables: Consider testing multiple variables simultaneously (e.g., subject line, email content, and send time).
Factorial Design: Use factorial designs to test combinations of variables and identify interactions.
Implement Tracking:
Advanced Metrics: Track more advanced metrics like customer lifetime value, revenue per user, or engagement rate.
Run the Experiment:
Longer Duration: Run experiments for a longer period to capture long-term effects.
Analyse Results:
Statistical Analysis: Use statistical tests like t-tests or ANOVA to analyse the significance of results.
Data Visualisation: Create visualisations to communicate insights effectively.
Advanced Level
Develop a Comprehensive Experiment Plan:
Detailed Protocol: Create a detailed experimental protocol outlining the hypothesis, design, data collection, and analysis plan.
Consider Experimental Design:
Complex Designs: Use advanced designs like randomised block designs or split-plot designs to control for confounding variables.
Implement Robust Tracking:
Custom Metrics: Develop custom metrics to measure specific outcomes relevant to your business objectives.
Run the Experiment:
Ethical Considerations: Ensure experiments are conducted ethically and comply with data privacy regulations.
Analyse Results:
Advanced Statistical Modelling: Use advanced statistical models like regression analysis or machine learning to uncover deeper insights.
Causal Inference: Employ causal inference techniques to draw stronger causal conclusions.
Remarkable Marketer of the Week:
Shane Murphy-Reuter
Shane Murphy-Reuter has vast experience in the marketing industry and his exemplary roles in both B2B at ADRoll, and B2C in online gaming speaks volumes. Today, he is the Senior Vice President (SVP) of marketing at Intercom (One of the biggest SaaS Companies in the world)
Remarkable Ideas
Shane Murphy-Reuter has been embracing impeccable concepts to help businesses grow, and they include:
Brand Alignment
Every company has to have a clear value proposition that works well with its brand, audience and products.
He uses this concept to help companies get their alignment right and stand an edge above their competitors. For instance, the message the company is passing across should be clear and consistent enough to build trust.
Shane asserts that it is the incredible real human connections at Intercom that pushed him to join the company. The company's clear focus on its core products and things like its logo makes it stand out.
Two Approaches to Marketing Messaging
Most marketers struggle with building effective marketing messages as they don’t focus on their product functions or what the products actually do.
He uses an approach where marketers focus their messaging on the impact of their products. In essence, customers will repay with loyalty if they are satisfied with the products at their disposal.
Shane also recommends marketers to grasp the key insights that make their brands and businesses grow. For instance, they need to develop a campaign concept and be able to communicate their emotional and functional brand positioning. The campaign they embark on should bring the ideas they embrace to life.
Consistent Messaging & Clear Differentiation
For Shane the idea of consistency in messaging is imperative to all marketers and the growth of a business. He advises marketers to have a clear differentiation that will help their businesses stand out in a crowded market.
Through consistent messaging, marketers should communicate the same message and with clarity. Your target audience or employees should understand the same message.
By being different you will be able to spend more to attract more customers and add new products your competitors can't offer. With a clear differentiation, you will subtract something and push your business to a higher rank. You can also speed up your offers and even raise your prices to rank at the top in a competitive market.
Connect with Shane Murphy-Reuter
To learn more about marketing, the concepts to embrace and how to stand out in a crowded market, it's easy and convenient to connect with Shane on his website, Twitter or LinkedIn.
Marketing Tool Of The Week : Heap.io
Tool description
Heap.io is a product analytics platform that help you track and use your audience behavioral data for product development and optimization.
It allows you to can retroactively name and manage user interactions/event without coding.
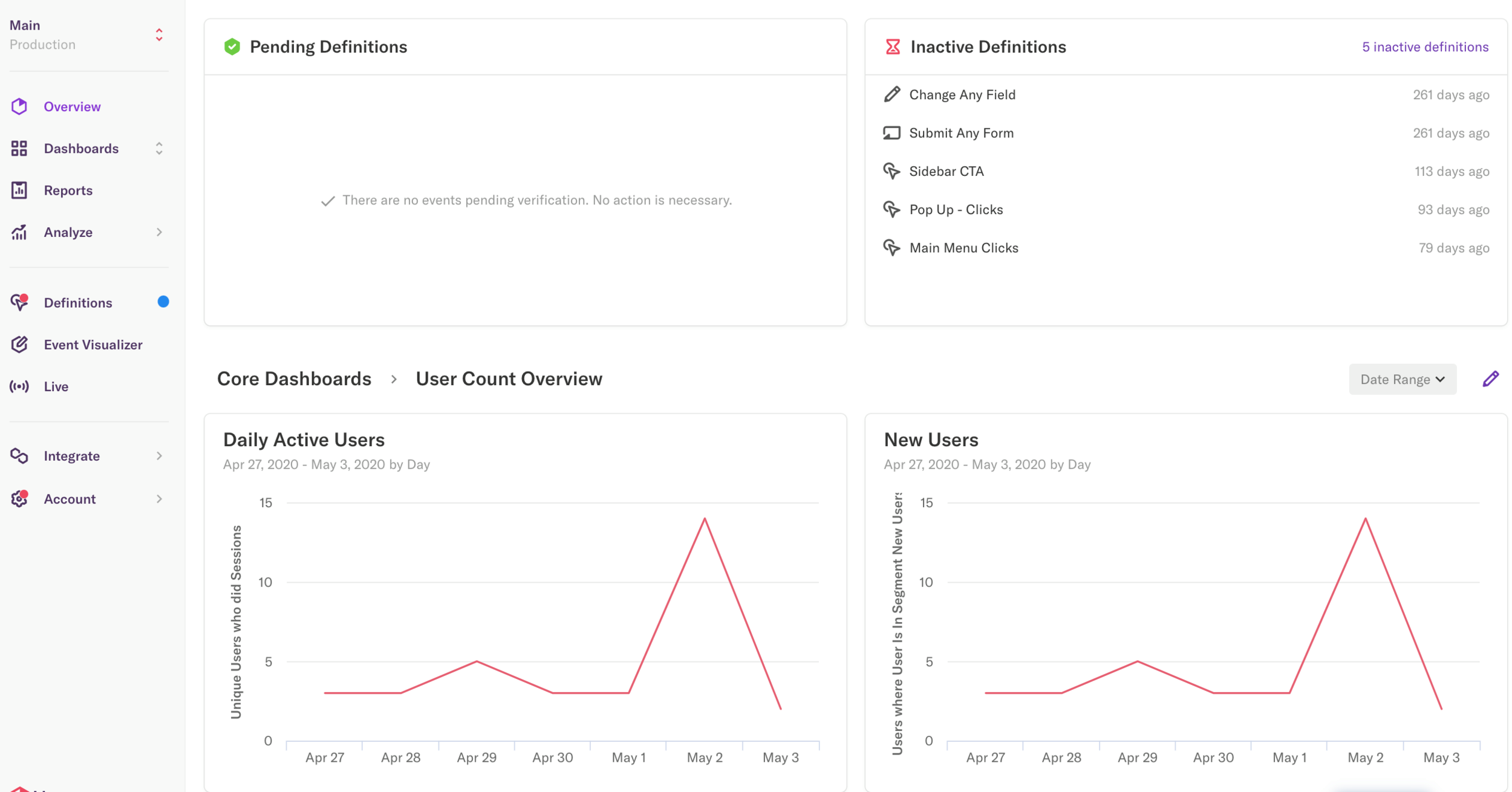
Heap.io - Overview Dashboard
It provides meaningful insights about the way people interact with your products, which helps you improve your acquisition & retention efforts, by creating a secure product experience.
Heap.io provides a unique approach by storing all user's interactions and analyzing them fast. The data is real-time, meaning that your reports are accurate and timely.
Heap has an easy interface, being easy to assemble queries and reports of all kinds. You will be able to access a complete dataset of user behavior.
Features
Let's take a closer look at the main features and benefits of this tool:
Capture all user data - it automatically captures all user data, including every click, swipe, tap, pageview, and fill. You will have access to all this without having engineers write elaborated codes. This data will provide you useful insight about your visitor journey on your website, finding out the strengths and weaknesses of the user experience.
Virtual events - you can manage your product data, by retroactively name and manage customer interactions. You can apply multiple labels to raw data without compromising it. This possibility gives you flexibility while keeping your dataset and your analyses clean and trustworthy. Virtualization is a smarter approach to analytics.
Heap.io - Retention Dashboard “Easily Create Retention Reports Curves”
Data governance - your data is safe and controlled with Heap Analytics. It provides for you reliable data with full control for viewing, modifying, and reporting. You can also keep your account clean and organized with categorized events, segments, reports, etc.. You can easily control who has access to your data, making sure that information is protected. Also, you can keep a current dataset, with the help of useful tools such as event page views, version control, and verification.
Security and compliance - this tool takes security very seriously, and you want this for your analytics provider. They invest in security technology, certifications, and personal training. Your data is safe and secure while you are using Heat Analytics, and this is a highly important feature.
Pricing
Heap Analytics has three pricing categories, as follows:
Free - for small businesses and side projects;
Growth - available for start-ups with under 20 employees;
Enterprise - for companies that rely on customer data and behavioral analytics.
You can contact them, depending on the business you run and get the exact price.
Heap.io - Pricing Page
Audience
We recommend Heap analytic for Marketers & Product Managers willing to have a better understanding of their product and websites retention and activation curves. It is a useful tool that provides deep insight into consumer behavior.
Alternatives
Here are some alternative to Heap Analytics,
Pendo - Similar Functionality Complex on-boarding process. According to G2 reviewers, in comparison with Heap.io, is slower to reach ROI, but easier to do business with and has a better support.
Mixpanel - Similar outcome but a bit more complex in terms of event capturing and management. According to G2 reviewers, is slower to reach ROI and more expensive.
Amplitude Analytics - Similar Functionality and Outcomes. G2 Reviewers think Amplitude is more usable and has a better at support